Deep Learning for TS
Deep learning models are a family of neural network models that have multiple layers between the input and output layers. These layers allow the model to learn increasingly complex features and representations of the input data, making them effective for time series modeling where the data may have complex and nonlinear relationships. In time series modeling, deep learning models are used to automatically extract and learn features from the time series data, which can then be used for prediction or classification tasks. These models can be used to model both univariate and multivariate time series data.
Some common deep learning models used for time series modeling include recurrent neural networks (RNNs), long short-term memory networks (LSTMs), and gated recurrent unit networks (GRUs). This section is going to fit AZN stock price into these three deep learning models and explore meaningful results from the predictive modeling.
Deep Learning Codes
RNN
A simple RNN is a type of recurrent neural network that can be used as a time series model. In a simple RNN, each time step takes an input vector and a hidden state vector, which is updated based on the previous hidden state and the current input. The hidden state serves as a memory for the model, allowing it to capture dependencies and patterns in the time series data.
The figures below shows the result of fitting AZN stock price into RNN model.
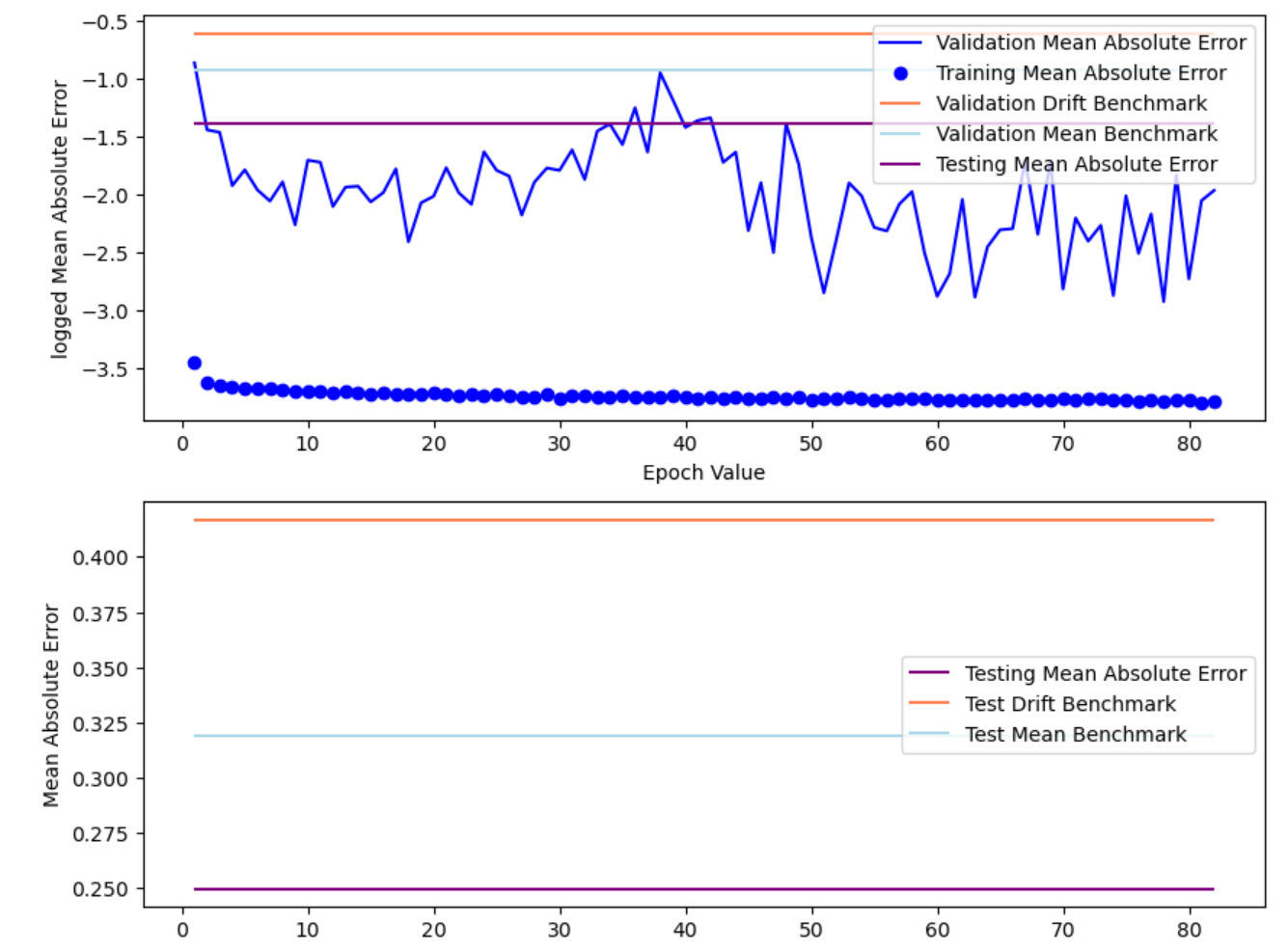
The model has: Train RMSE: 0.028; Test RMSE: 0.172
RNN with L1 regularization
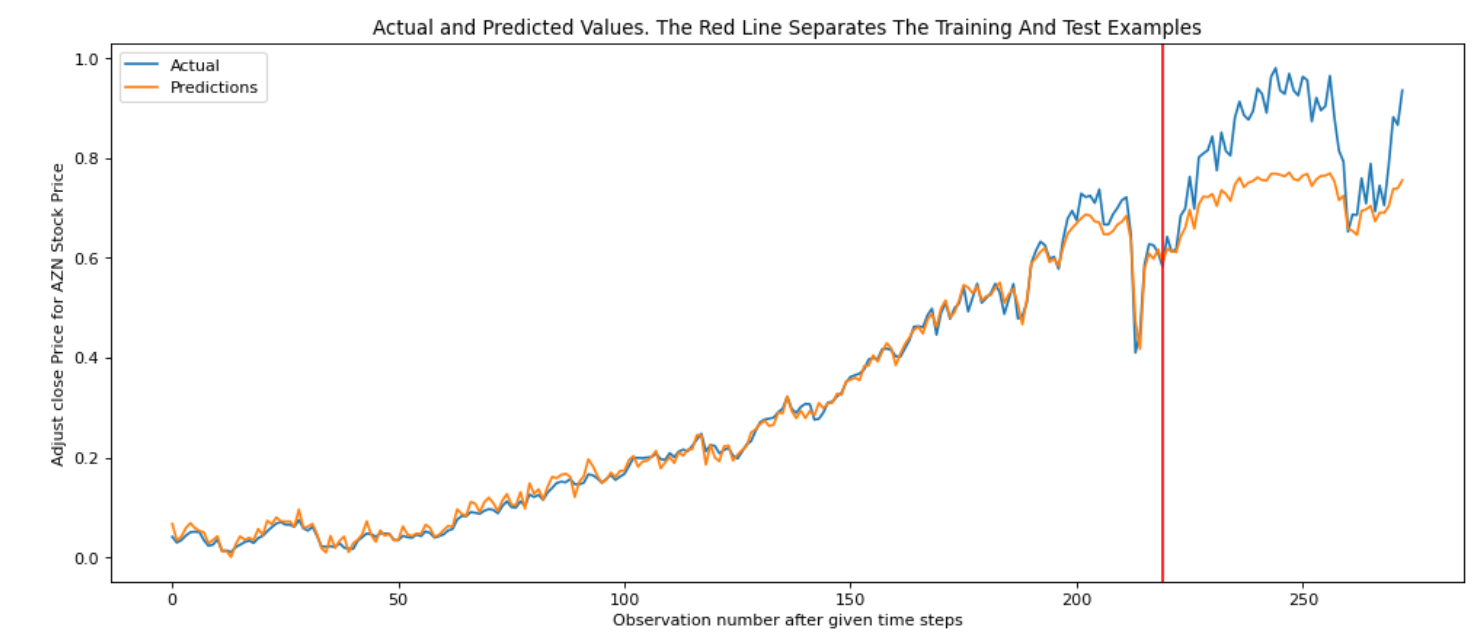
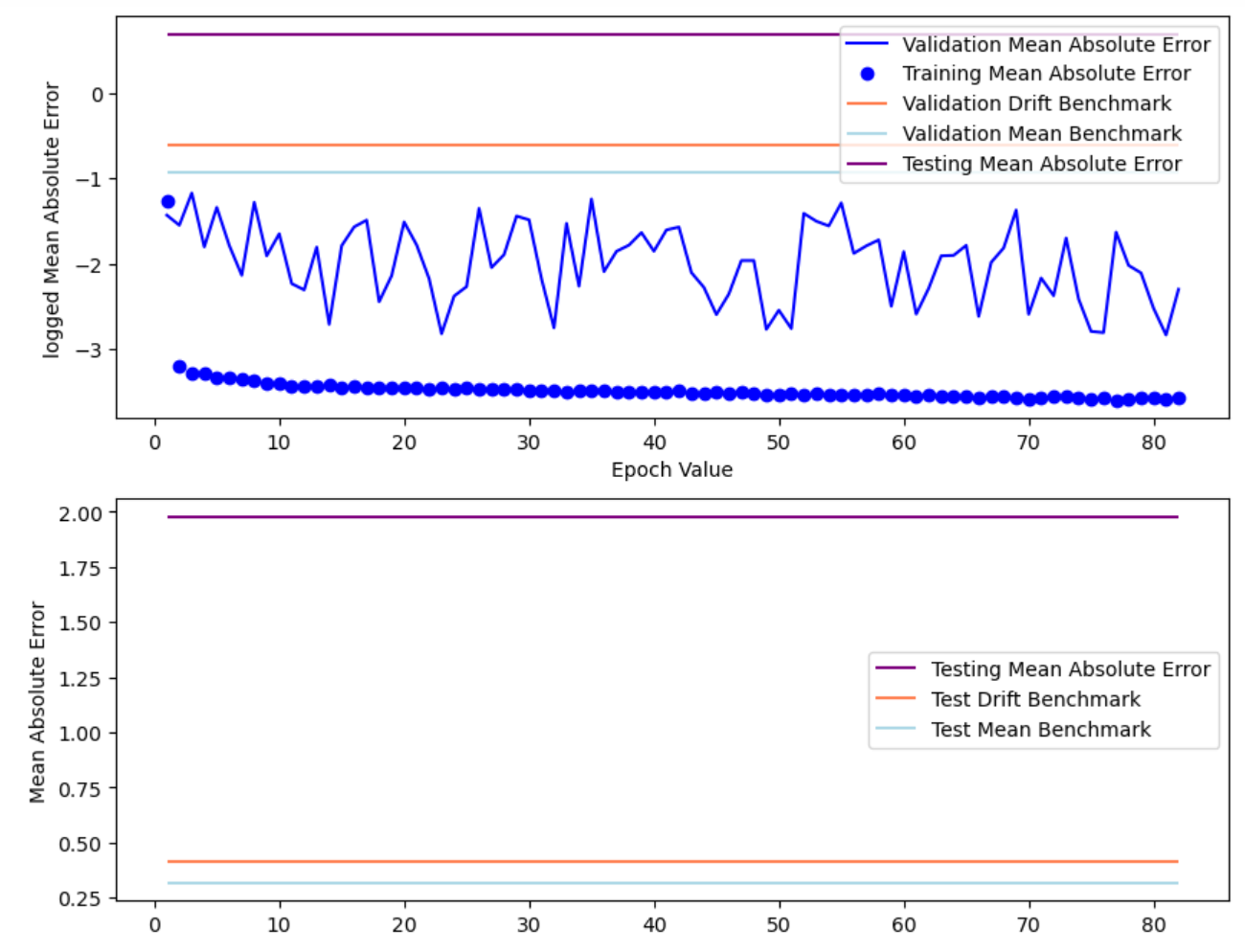
This section add both L1 and L2 regularization to simple RNN model to avoid overfitting. Generally, RNN with L2 regularization have lower error measurement comparing to the simple RNN model, while L1 regularization have higher error test RMSE than the simple RNN model.
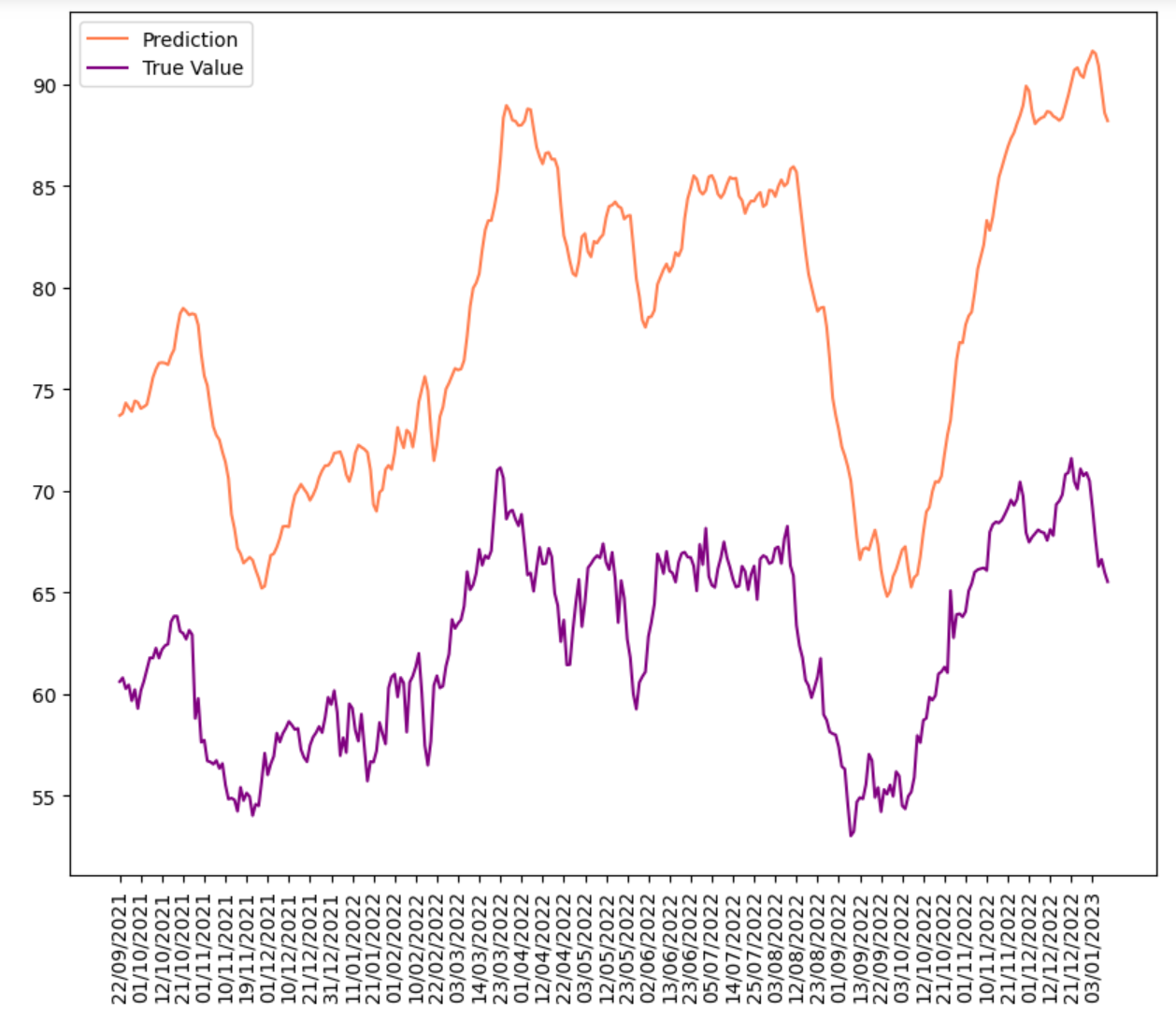
The model has: Train RMSE 0.011; Test RMSE: 0.571
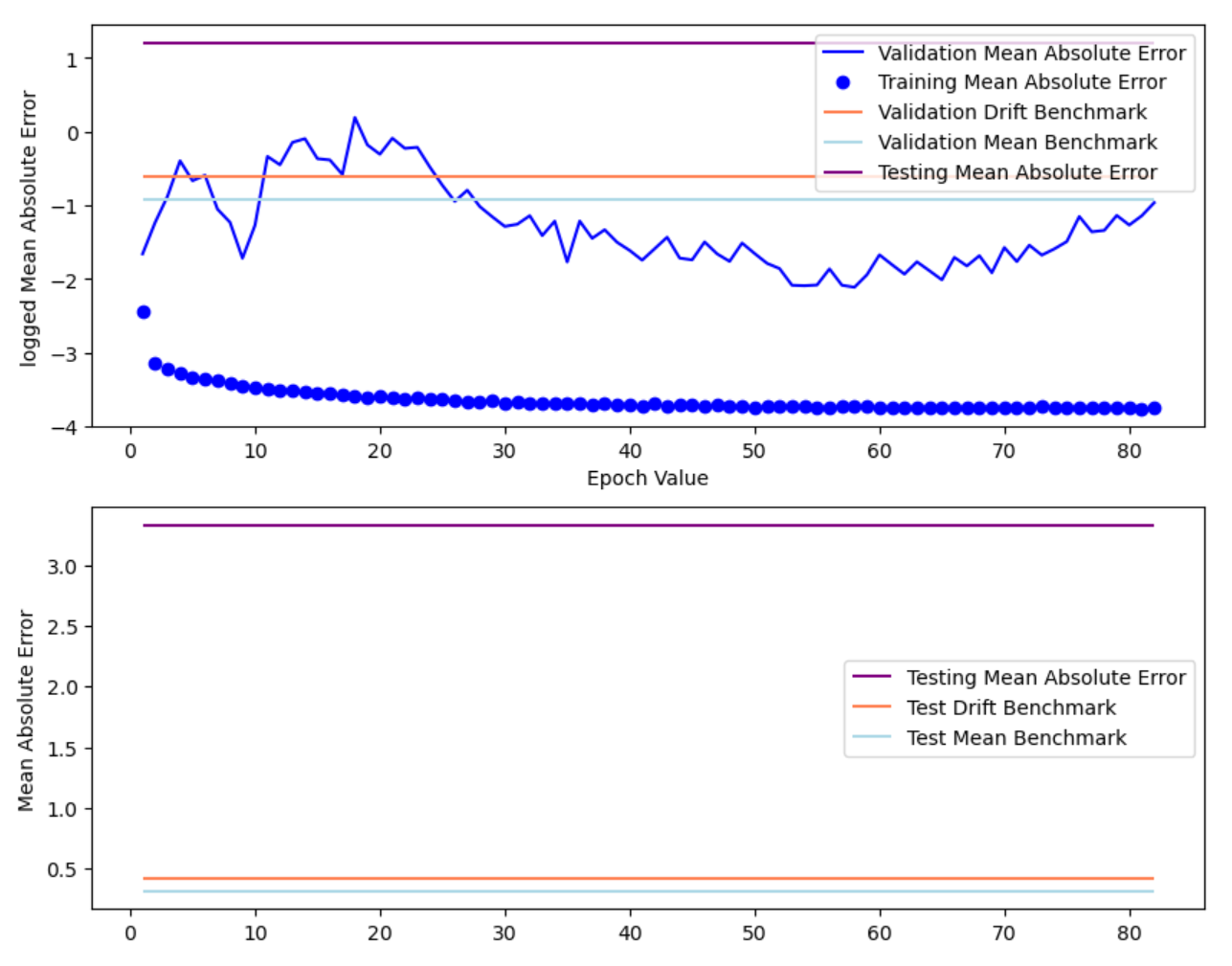
RNN with L2 regularization
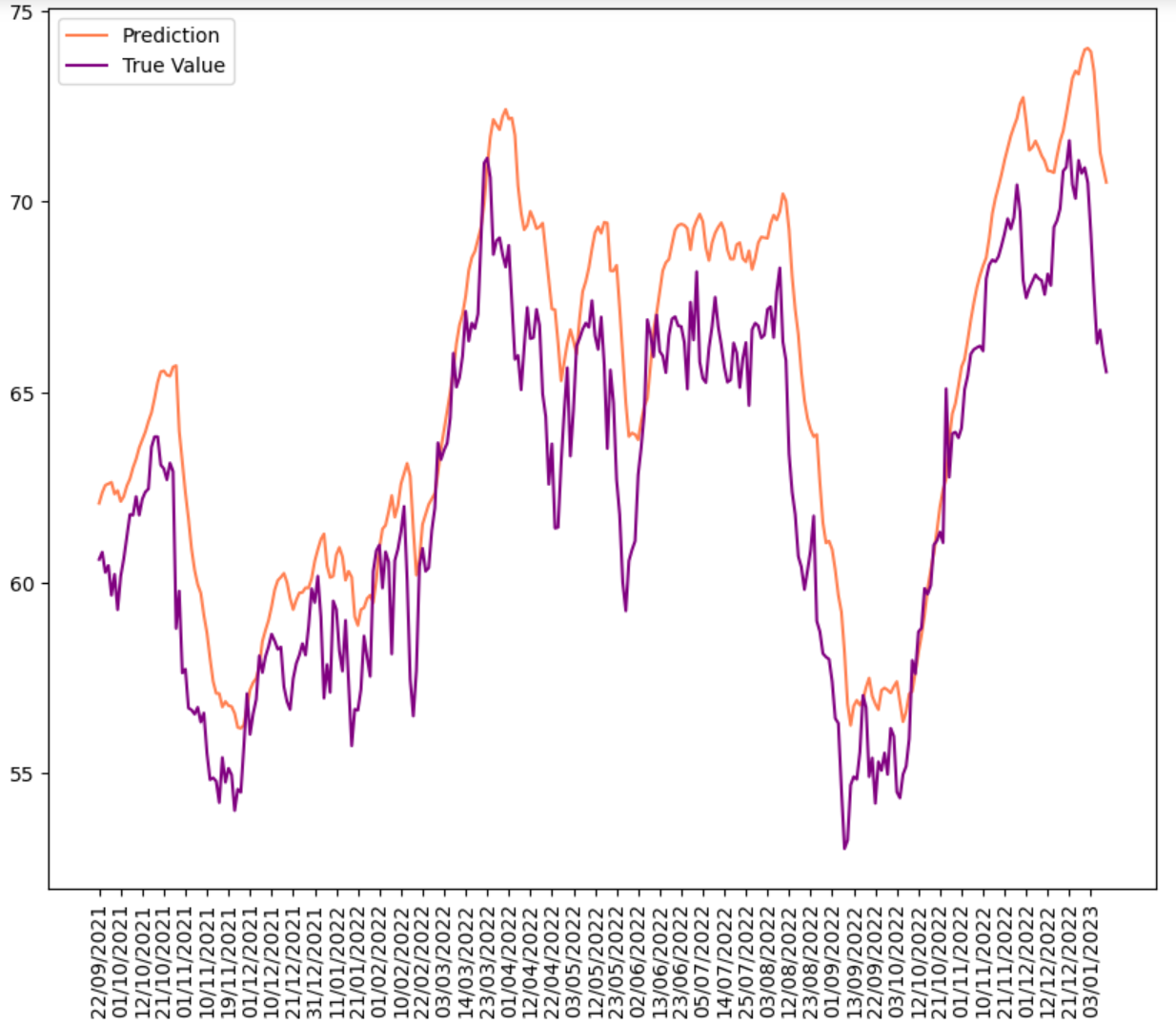
The model has: Training RMSE: 0.032; Testing RMSE: 0.047
LSTM
LSTM stands for Long Short-Term Memory, which is a type of recurrent neural network that is designed to address the issue of the vanishing gradient problem in simple RNNs when used for time series modeling. LSTM networks are particularly effective for modeling long-term dependencies and patterns in sequential data, such as time series data. In an LSTM network, each time step takes an input vector, a hidden state vector, and a cell state vector, which are updated based on the previous hidden state, cell state, and the current input. The cell state serves as a long-term memory for the model, allowing it to capture and remember important information about the time series data over long periods of time. The hidden state, on the other hand, serves as a short-term memory that allows the model to capture short-term patterns and dependencies in the data.
The figures below shows the result of fitting AZN stock price into LSTM model.
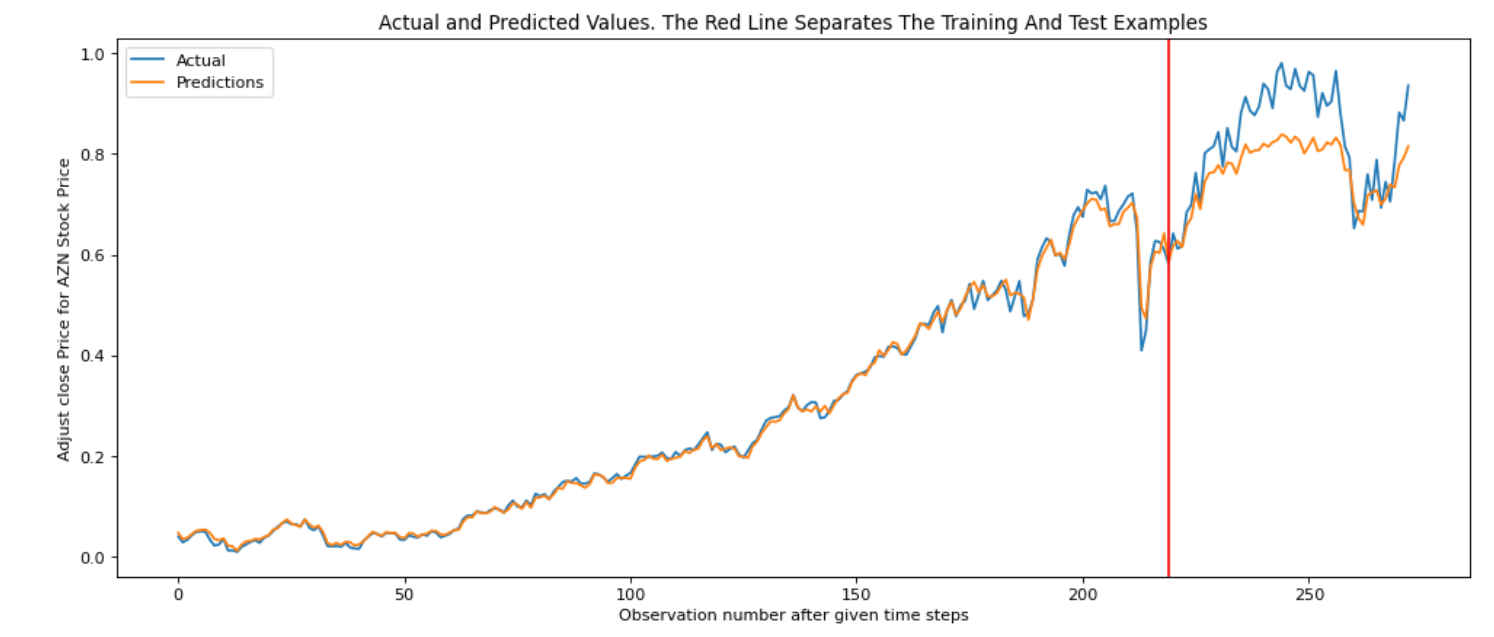
The model has: Train RMSE: 0.012; Test RMSE: 0.079
GRU
GRU stands for Gated Recurrent Unit, which is a type of recurrent neural network that is designed to address the vanishing gradient problem in simple RNNs when used for time series modeling. GRU networks are similar to LSTM networks in that they use gates to control the flow of information in the network, but are computationally less expensive and have fewer parameters. In a GRU network, each time step takes an input vector and a hidden state vector, which are updated based on the previous hidden state and the current input. The GRU has two gates, a reset gate and an update gate, which control the flow of information into and out of the hidden state.
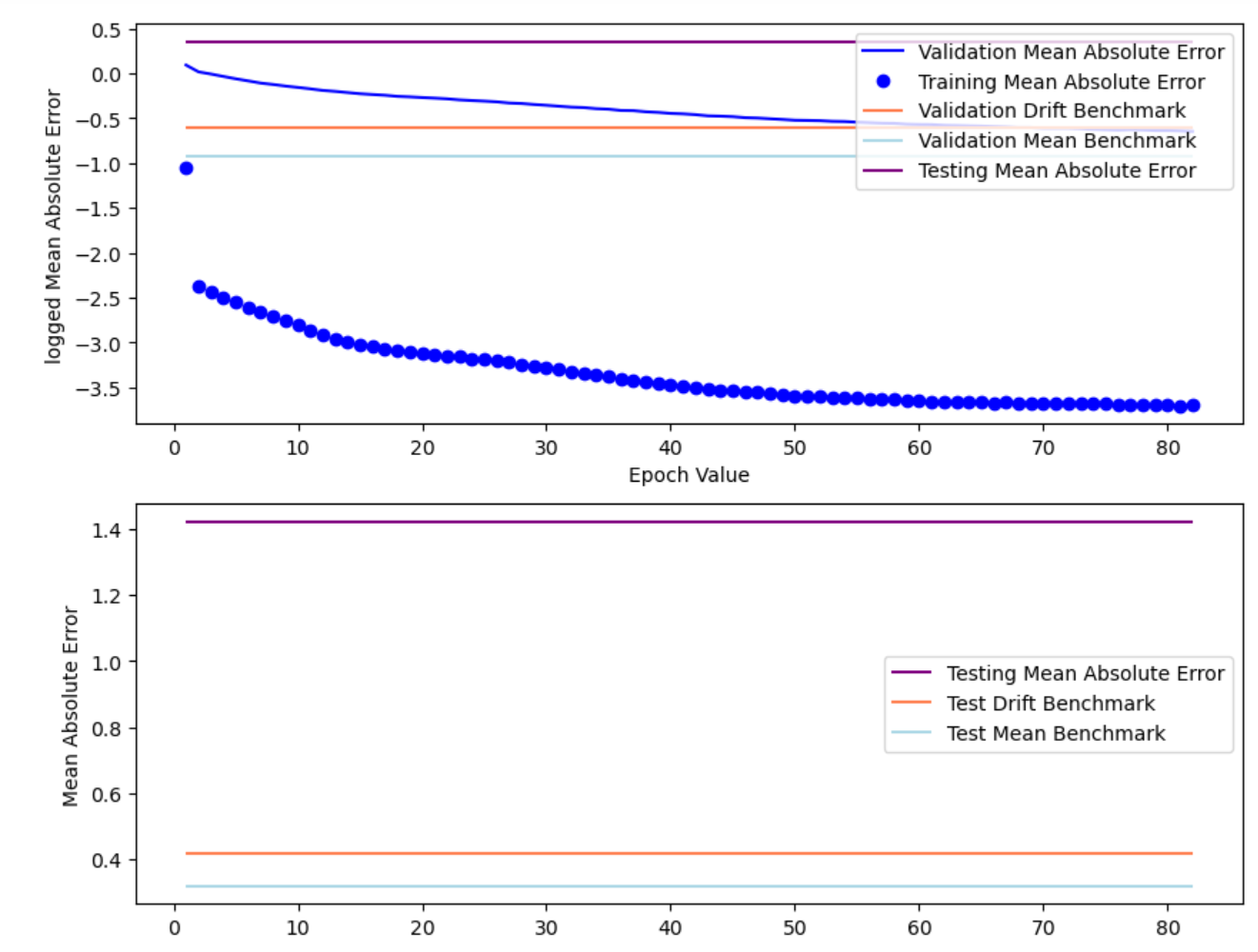
The figures below shows the result of fitting AZN stock price into GRU model.
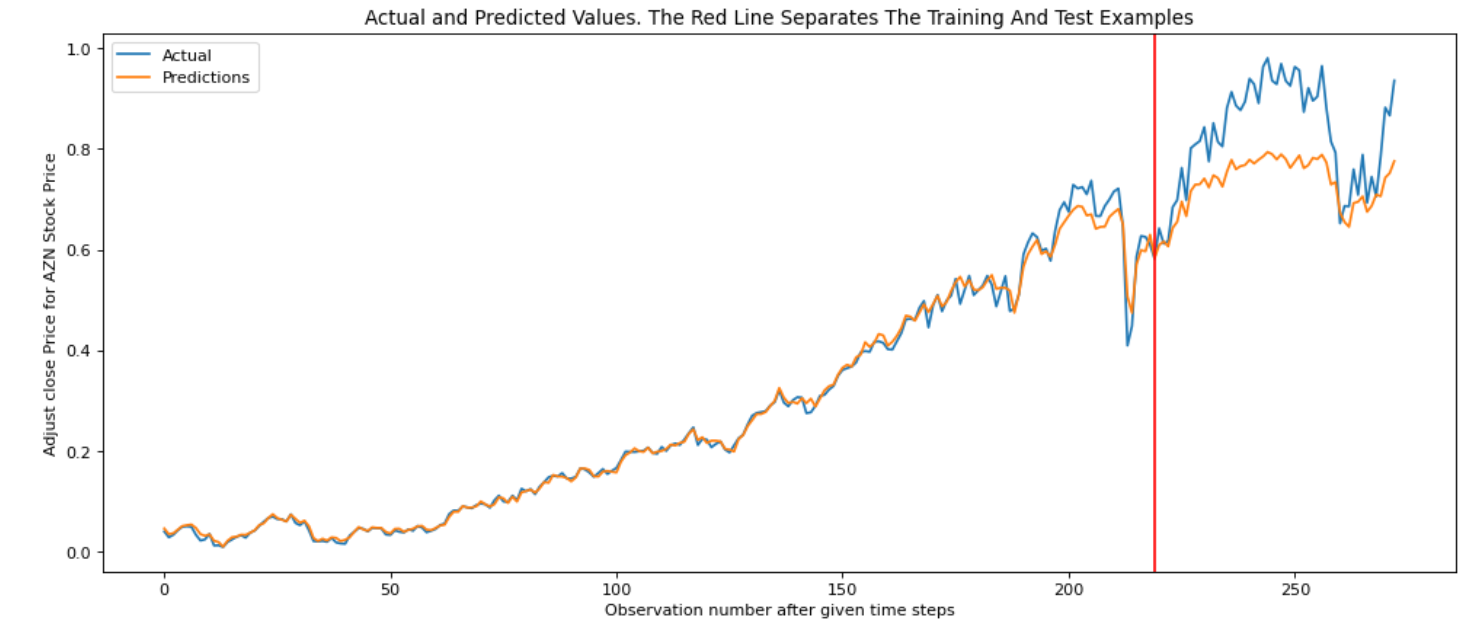
The model has: Train RMSE: 0.008; Test RMSE: 0.078
Result Discussion
| Model | Train RMSE | Test RMSE |
|---|---|---|
| RNN | 0.028 | 0.172 |
| RNN L1 | 0.011 | 0.571 |
| RNN L2 | 0.032 | 0.047 |
| LSTM | 0.012 | 0.079 |
| GRU | 0.008 | 0.078 |
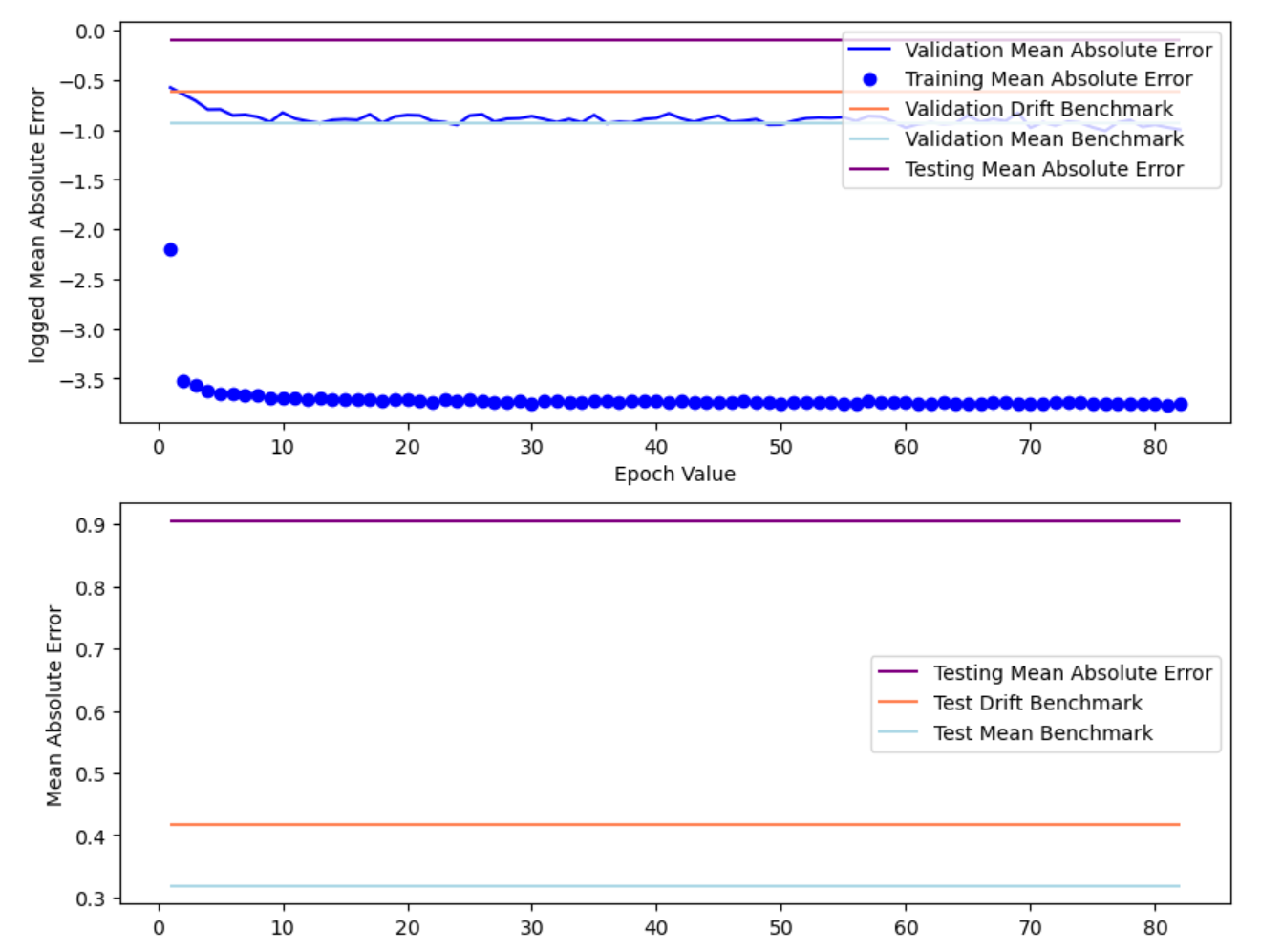
Overall, GRU has the lowest test RMSE (0.078) among all three models, LSTM ranks the second (0.079), and simple RNN has the highest test RMSE (0.172). Besides, RNN with L2 regularization has the lowest test RMSE (0.047).
In general, deep learning models can make accurate predictions for horizons ranging from a few time steps to several hundred time steps, but the accuracy may decrease as the forecasting horizon increases.
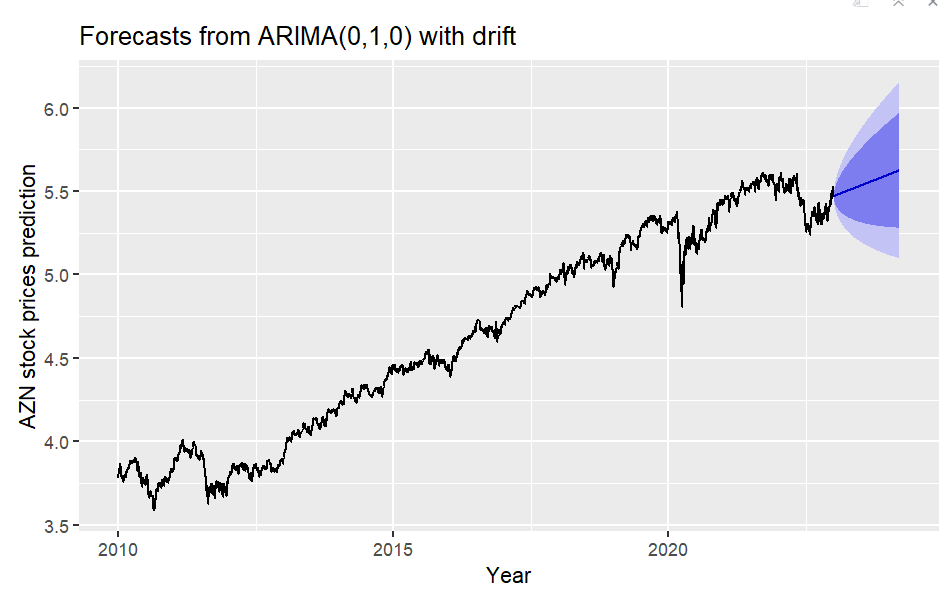
Deep Learning VS ARIMA
Here is the comparison plots between the ARIMA Model and Deep Learning methods. GRU method was chosen here since it works best in all the deep learning methods. According to error measurement, deep learning methods (RMSE 0.008) slightly outperforms the ARIMA model (0.016). However, the ARIMA model is more straightforward than a neural network with far fewer parameters and easier to understand. It can be concluded that both method have shown that it is very likely to have an up-ward trend for AZN stock price in the near future. An ARIMA model is far easier to set up and should be considered, especially with its ability to be interpretable, but a neural network is an excellent alternative.